GitHub
GitHub is one of Palmr's officially supported OIDC providers, offering secure authentication through GitHub OAuth 2.0. This integration allows users to sign in to Palmr using their existing GitHub accounts, making it perfect for developer teams, open-source projects, and organizations already using GitHub for version control and collaboration.
Why use GitHub authentication?
GitHub authentication provides several advantages for developer-focused organizations and teams:
- Developer-friendly - Perfect for teams already using GitHub for development
- Open-source integration - Ideal for open-source projects and communities
- Rich developer profiles - Access to GitHub usernames, avatars, and organization memberships
- Repository access - Can leverage GitHub's permission system for additional features
- No additional accounts - Developers can access Palmr with their existing GitHub credentials
Prerequisites
Before configuring GitHub authentication, ensure you have:
- GitHub account - Ability to create OAuth Apps on GitHub
- Admin privileges in Palmr - Required to configure OIDC settings
Note: GitHub is pre-configured as an official provider in Palmr, which means the technical configuration is handled automatically. You only need to provide your OAuth credentials.
Setting up GitHub OAuth App
Creating a GitHub OAuth App
To get started with GitHub authentication, you'll need to create an OAuth App in your GitHub Developer Settings.
-
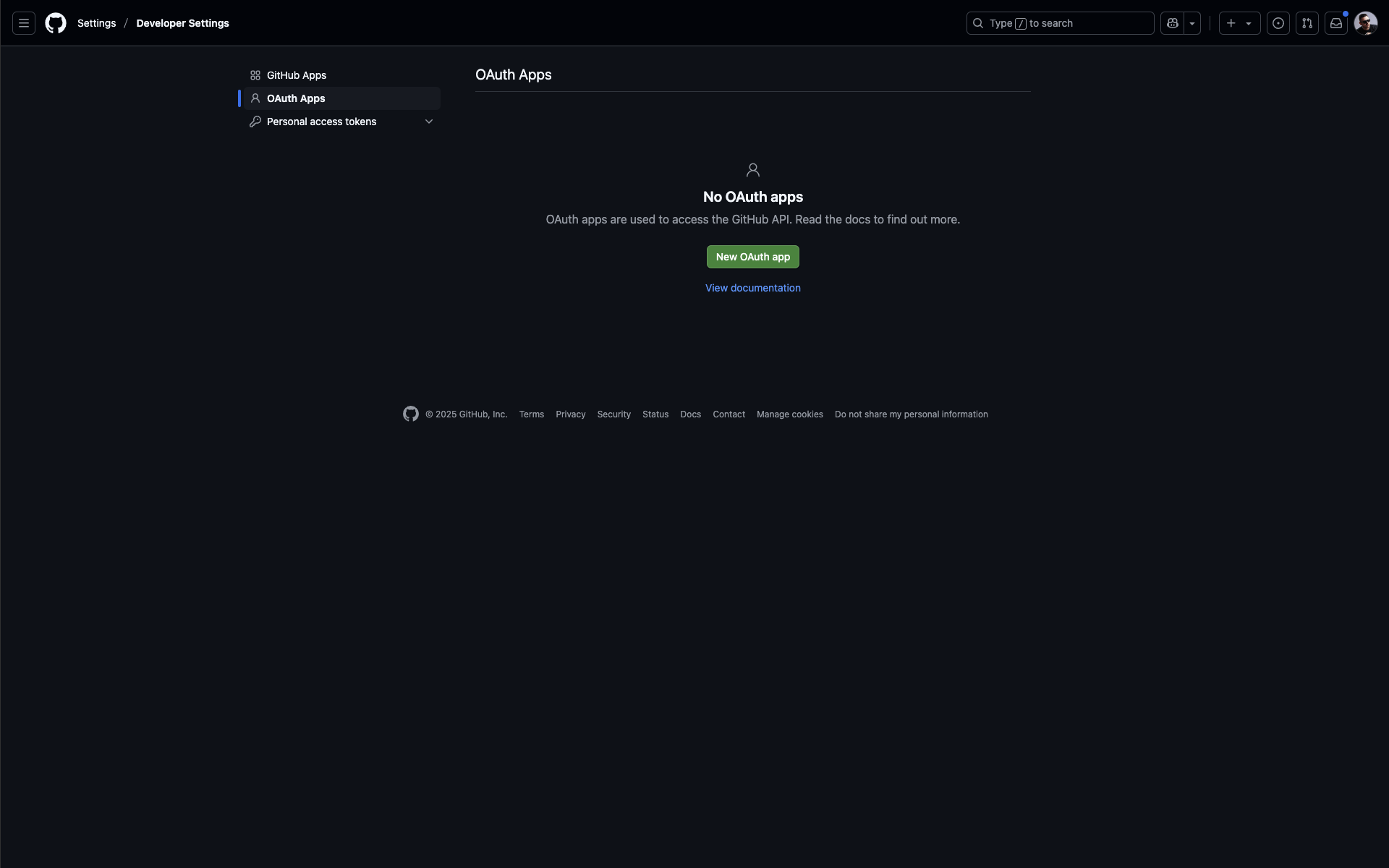
Navigate to GitHub Developer Settings: Go to github.com/settings/developers
-
Create new OAuth App: Click "New OAuth App" button
- Enter application details:
- Application name: Enter a descriptive name like "Palmr File Sharing"
- Homepage URL: Enter your Palmr instance URL (e.g.,
https://yourdomain.com) - Application description: Add a clear description of your Palmr instance
- Authorization callback URL: Enter your callback URL (see below)
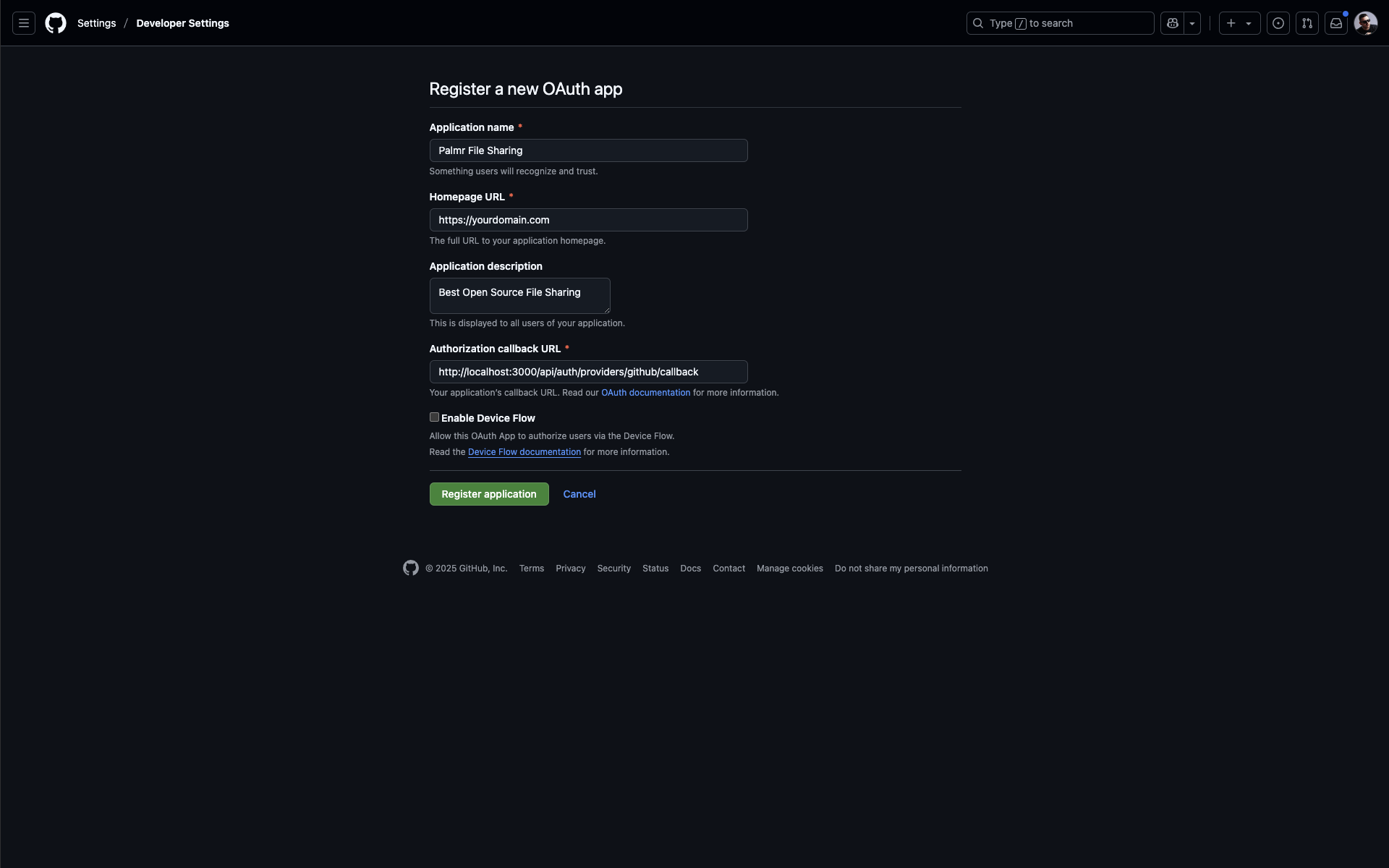
This is a fake application, you have to use your own.
Set up callback URLs: In the "Authorization callback URL" field, add your Palmr callback URL:
You'll need to configure several URLs in your GitHub OAuth App settings. Here's what to add for each environment:
Authorization Callback URLs
| Environment | URL |
|---|---|
| Production | https://yourdomain.com/api/auth/providers/github/callback |
| Development | http://localhost:3000/api/auth/providers/github/callback |
| Custom Port | https://yourdomain.com:5487/api/auth/providers/github/callback |
Note: Replace
yourdomain.comwith your actual domain name in all production and custom port URLs. Note: You can add multiple callback URLs for different environments (development, staging, production).
- Create application: Click "Register application" to generate your OAuth App
Getting OAuth credentials
Now you'll get the credentials that Palmr will use to authenticate with GitHub.
-
Copy Client ID: The Client ID is displayed on your OAuth App page
-
Generate Client Secret: Click "Generate a new client secret" to create a new secret
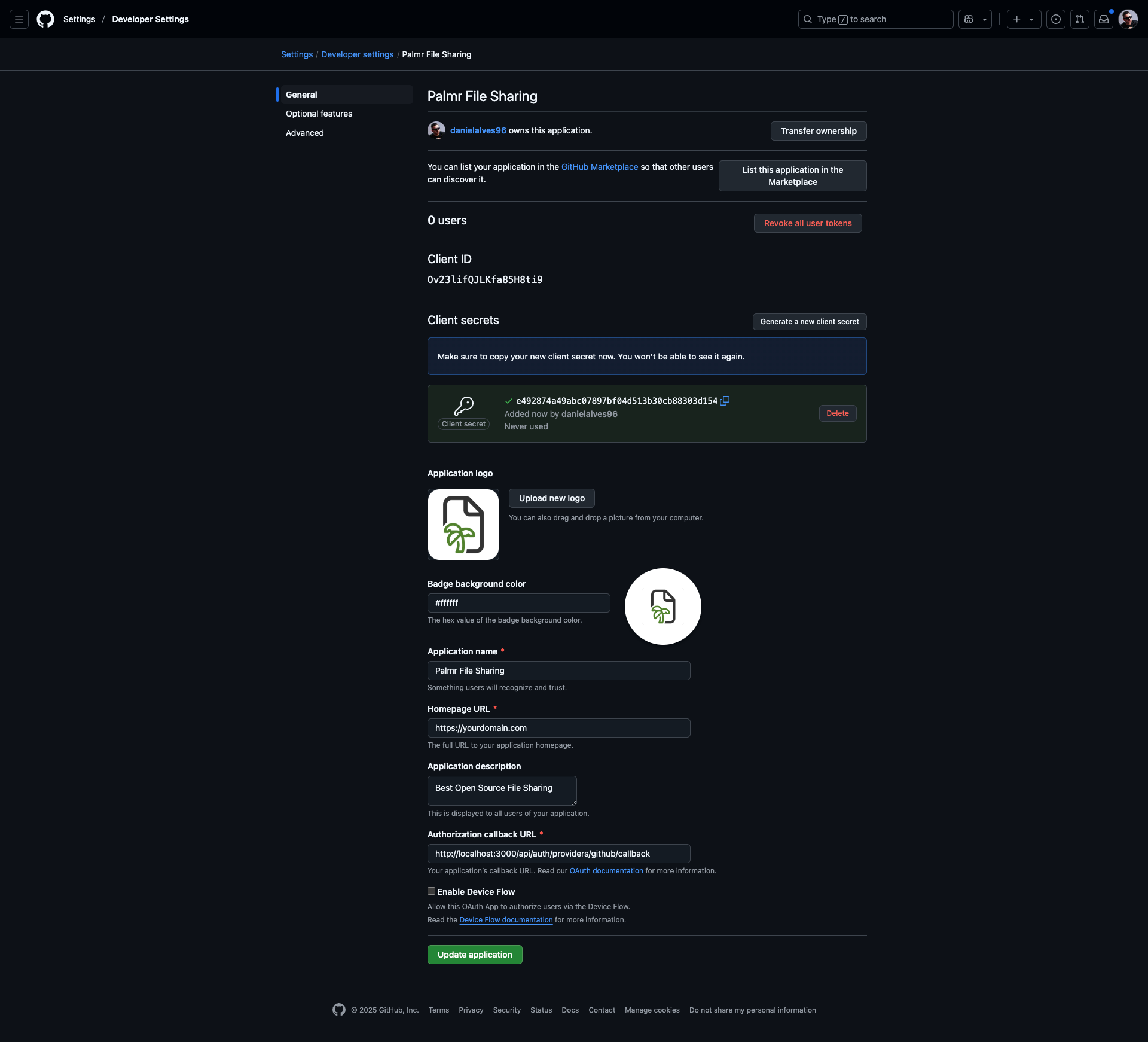
The client ID and client secret shown in the image are examples only (fake credentials). You must use your own credentials from GitHub.
- Save credentials: Copy both the Client ID and Client Secret for later use
Important: Replace
yourdomain.comwith your actual domain. You can add multiple callback URLs for different environments (development, staging, production) by creating separate OAuth Apps.
Configuring Palmr
Accessing OIDC settings
To configure GitHub authentication in Palmr, you need administrator access to the settings panel.
-
Login as administrator: Sign in to Palmr with an admin account
-
Access settings: Click your profile picture in the header and select Settings
-
Navigate to authentication: Find and click on the Authentication Providers configuration section
Enabling GitHub provider
GitHub comes pre-configured as an official provider, so the setup process is streamlined.
-
Locate GitHub provider: Find GitHub in the list of available providers
-
Enable the provider: Toggle the status to Enabled
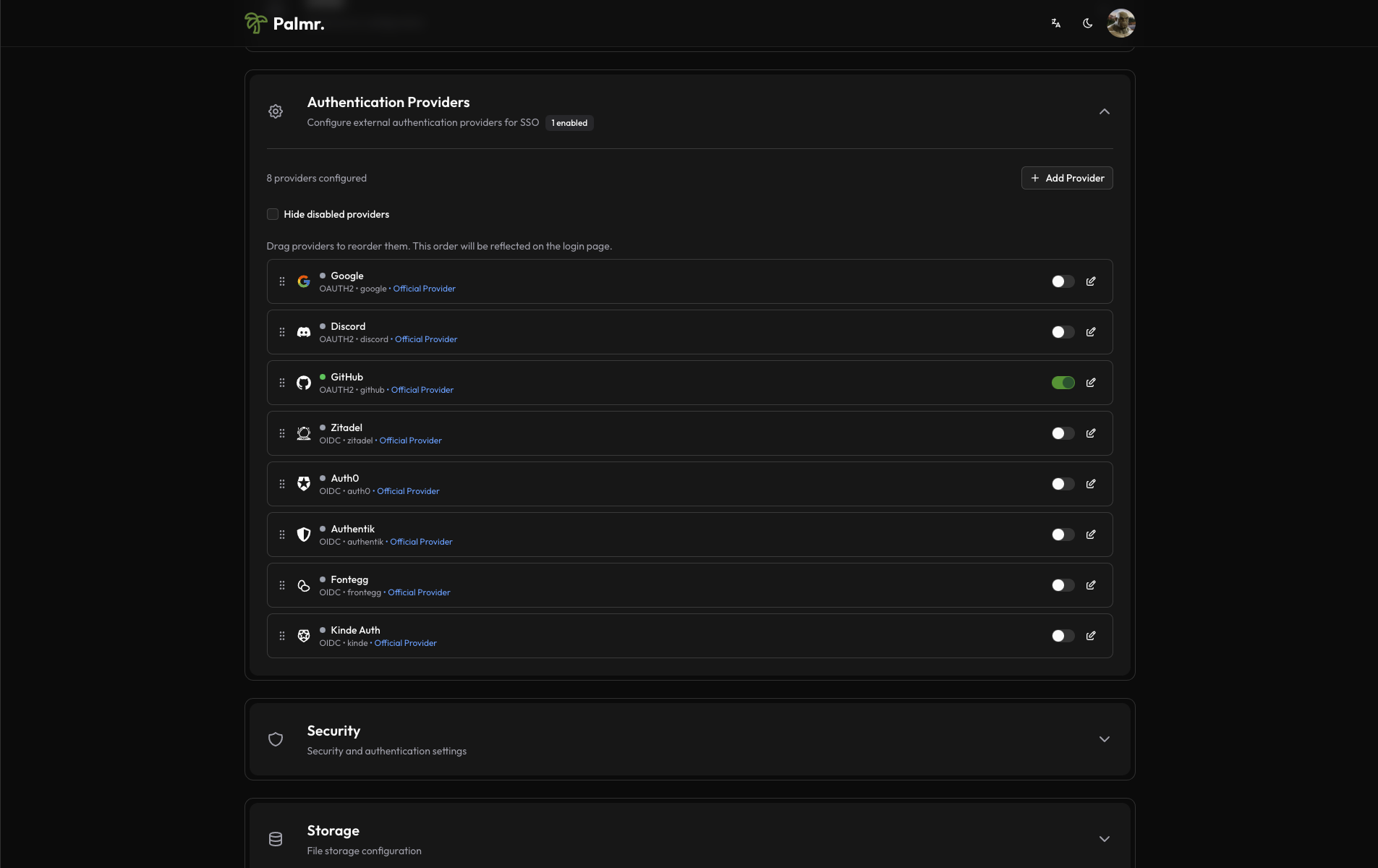
After enabling the provider, click on the pen icon to configure the provider.
- Configure credentials:
- Client ID: Paste the Client ID from GitHub OAuth App
- Client Secret: Paste the Client Secret from GitHub OAuth App
- Scopes: Add the scopes you want to use. The default scopes are
user:email.
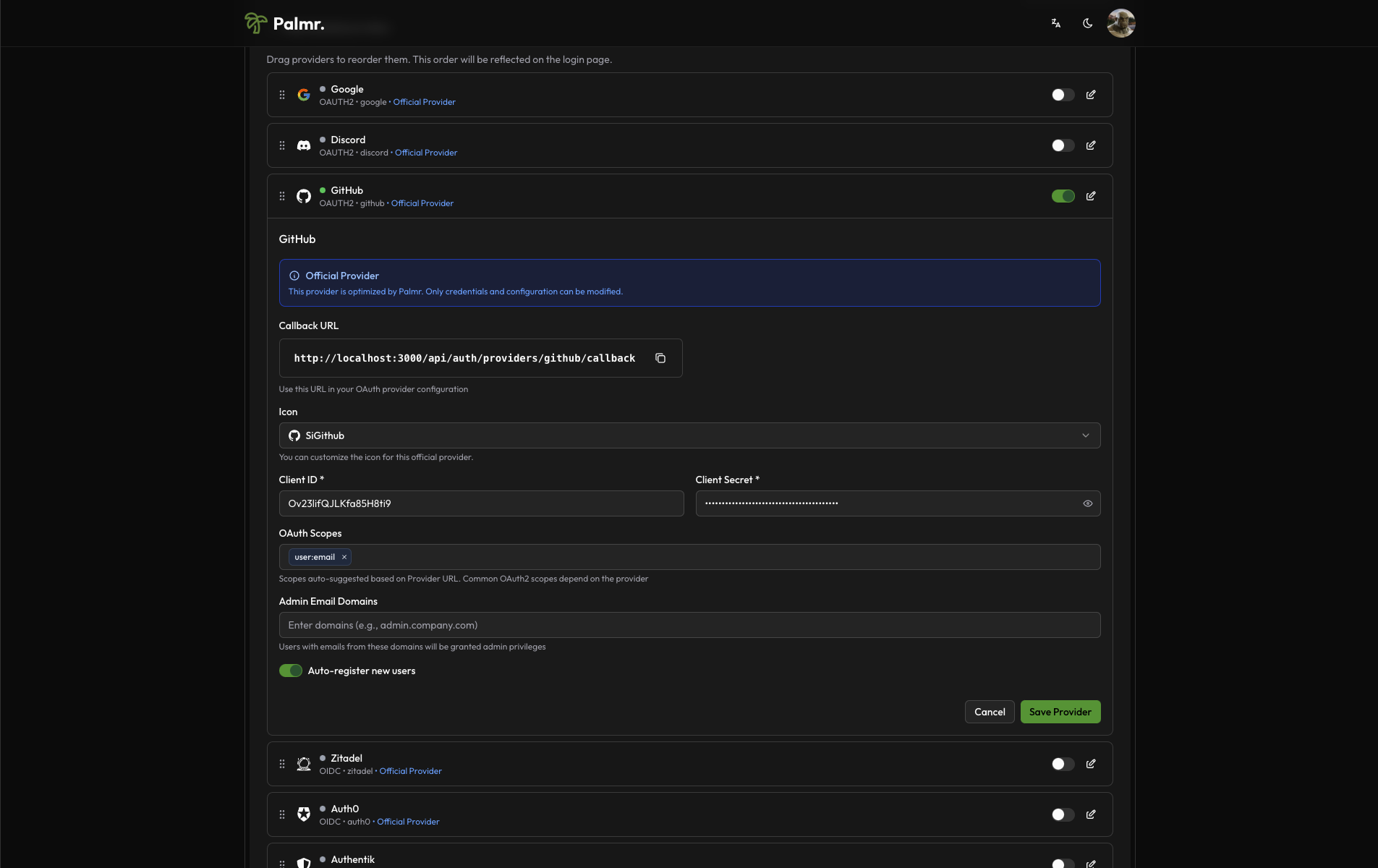
This is a fake application, you have to use your own.
Advanced configuration options
Configure additional settings to customize the authentication behavior:
Auto Registration: Enable this to automatically create user accounts when someone authenticates for the first time.
Admin Email Domains: Specify domains that should automatically receive admin privileges. For example, entering yourcompany.com will grant admin access to anyone with an email from that domain.
Sort Order: Control where the GitHub login button appears relative to other authentication providers.
Icon: you can choose the icon you want to use for the GitHub login button (default is SiGithub).
Developer tip: GitHub authentication works great for development teams and open-source projects.
Account linking
By default, if a user is already registered in Palmr with their GitHub email, they will be automatically linked to their Palmr account.
Note: You can't disable account linking. If you want to unlink a user from their GitHub account, you need to delete the user from Palmr.
Technical configuration
GitHub's technical configuration is handled automatically, but understanding the setup can help with troubleshooting:
Field mappings
Palmr automatically maps GitHub user information to local user accounts:
- User ID: Maps from GitHub's
idfield - Email: Maps from GitHub's
emailfield (from user:email scope) - Full Name: Maps from GitHub's
namefield - Username: Maps from GitHub's
loginfield - Avatar: Maps from GitHub's
avatar_urlfield
Testing the configuration
Verifying the setup
After configuring GitHub authentication, test the integration to ensure everything works correctly.
-
Check login page: Navigate to your Palmr login page and verify the "Sign in with GitHub" button appears
-
Test authentication flow: Click the GitHub sign-in button and complete the authentication process
-
Verify user creation: Confirm that a new user account is created (if auto-registration is enabled)
Login flow verification
The complete authentication process should work as follows:
- User clicks "Sign in with GitHub": The browser redirects to GitHub's authorization page
- User authorizes application: User grants permissions for the requested scopes
- GitHub redirects back to Palmr: User returns to Palmr with authentication tokens
- Palmr creates or updates user: User account is automatically managed with GitHub information
- User accesses Palmr: User is logged in with their GitHub identity
Troubleshooting common issues
Redirect URI mismatch error
Error message: The redirect_uri MUST match the registered callback URL for this application
Cause: The redirect URI in your request doesn't match what's configured in GitHub OAuth App.
Solution:
- Check the exact URL in the error message
- Add this exact URL to your GitHub OAuth App's callback URL
- Ensure you include the correct protocol (http/https) and port
- Remove any trailing slashes unless they're in the callback URL
Access denied error
Error message: access_denied
Cause: User denied permissions or the OAuth App isn't properly configured.
Solution:
- Verify that your GitHub OAuth App requests the correct scopes
- Check that users are granting permissions during the authorization flow
- Ensure your OAuth App is not restricted or disabled
- Verify the application has proper permissions set up
Invalid client error
Error message: invalid_client
Cause: Incorrect Client ID or Client Secret.
Solution:
- Double-check that you've copied the credentials correctly from GitHub
- Ensure there are no extra spaces or characters in the credentials
- Generate a new Client Secret if necessary
- Verify you're using the correct OAuth App in GitHub
Email not available error
Error message: Email not provided or scope missing
Cause: GitHub OAuth App not configured with user:email scope or user's email is private.
Solution:
- Verify that your GitHub OAuth App requests the
user:emailscope - Check that users have public email addresses or have granted email access
- Ensure the scope configuration matches what Palmr expects
- Test with a GitHub account that has a public email address
Security best practices
Credential management
- Never expose secrets: Keep your Client Secret secure and never commit it to version control
- Rotate credentials regularly: Generate new Client Secrets periodically for enhanced security
- Use environment variables: Store sensitive configuration in environment variables, not config files
- Monitor access logs: Regularly review authentication logs for suspicious activity
Scope and permission management
- Minimal scopes: Only request
user:emailscopes as required by Palmr - User consent: Ensure users understand what permissions they're granting
- Regular audits: Review which users have connected their GitHub accounts
- Access reviews: Periodically check user access and remove inactive accounts
Production considerations
- Use HTTPS: Always use HTTPS in production environments
- Configure proper domains: Use production domains in GitHub OAuth App
- Test thoroughly: Verify the complete authentication flow before going live
- Plan for failures: Have fallback authentication methods available
Next steps
With GitHub authentication configured, you might want to:
- Configure additional providers: Set up other OIDC providers for more authentication options
- Customize user management: Fine-tune auto-registration and admin assignment rules
- Review security settings: Ensure your authentication setup meets your security requirements
- Monitor usage: Keep track of authentication patterns and user activity
For more information about OIDC authentication in Palmr, see the OIDC Authentication overview.